158.63.258.200 – IP Address Explained!
158.63.258.200 is an invalid IPv4 address because one octet exceeds the allowed 0–255 range. It may appear in logs due to typos, misconfigurations, or parsing errors.
When you search for 158.63.258.200, one of the first questions that comes to mind is:
Is this a real IP address, or is it invalid?
Many users notice this IP appearing in:
- Server logs
- Network monitoring tools
- Firewall alerts
- Website analytics
- Security reports
At first glance, it looks like a normal IPv4 address. But technically, 158.63.258.200 is not valid.
In this detailed guide, we will explain:
- What 158.63.258.200 means
- Why it is considered an invalid IP address
- How IPv4 structure works
- Security implications of invalid IPs
- How to validate and fix IP addressing errors
- The shift from IPv4 to IPv6
Let’s break it down step by step.
What Exactly is an IP Address?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical identifier assigned to devices connected to a network.
It helps computers communicate with each other, just like a postal address helps deliver mail.
For example:
- Your phone has an IP address
- Your router has an IP address
- Websites and servers have IP addresses
Without IP addresses, the internet would not function properly.
Two main types of IP addresses:
- IPv4 (most common)
- IPv6 (newer version)
The IP 158.63.258.200 looks like IPv4, which brings us to the next section.
The Basics of IPv4 Structure
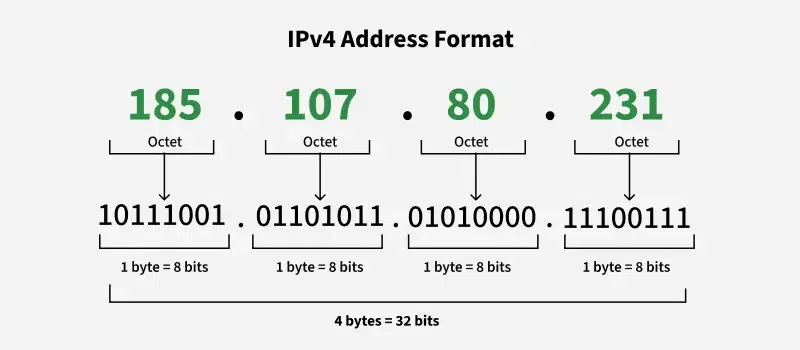
IPv4 addresses are written in this format:
X.X.X.X
Each “X” is called an octet, and each octet must follow strict rules.
Example of a valid IPv4 address:
192.168.1.1
IPv4 Octet Range Rule
Each octet must be a number between:
✅ 0 and 255
So valid ranges look like:
- 0
- 25
- 158
- 200
- 255
But never:
❌ 256
❌ 300
❌ 999
This rule is the key reason why 158.63.258.200 is invalid.
Why is 158.63.258.200 Considered Invalid?
Let’s look at the IP: 158.63.258.200
Break it into octets:
- 158 ✅
- 63 ✅
- 258 ❌
- 200 ✅
The problem is the third octet:
258 is outside the allowed IPv4 range (0–255)
That means:
🚫 158.63.258.200 is not a real IP address
🚫 It cannot exist in IPv4 networking
🚫 No device can legally use it
So technically, this is a malformed or invalid IPv4 address.
Why Do Invalid IPs Like 158.63.258.200 Appear?
If it’s invalid, you may wonder: Why does it show up in system logs or network reports?
Invalid IPs appear more often than you think. Here are the most common reasons:
1. Typographical Errors
Sometimes people mistakenly type an IP incorrectly, such as:
- 158.63.258.200 instead of 158.63.248.200
- Misplacing digits
This is one of the most frequent causes.
2. Placeholder or Dummy Data
Developers may use fake IP addresses in:
- Examples
- Documentation
- Testing environments
So 158.63.258.200 might appear as a placeholder.
3. Log Parsing Issues
Some tools incorrectly interpret data and record malformed IPs.
For example:
- Broken scripts
- Incorrect log formatting
- Data corruption
This leads to log anomalies.
4. Misconfigured Network Devices
Routers, proxies, or servers may produce invalid IP outputs if misconfigured.
This can happen in:
- Firewall rules
- NAT settings
- Subnet configuration errors
5. Malicious Activity or Spoofing Attempts
Attackers sometimes generate fake IPs to confuse security systems. While spoofing invalid IPs is uncommon, unusual addresses may still appear during scanning attempts.
Common Mistakes When Dealing with IP Addresses
Many network administrators and beginners make mistakes like:
- Confusing IPv4 and IPv6 formats
- Using numbers above 255
- Copying IPs incorrectly from logs
- Not validating IP addresses before applying rules
- Misunderstanding subnet ranges
These mistakes often result in invalid IP addresses such as 158.63.258.200.
The Implications of Using an Invalid IP Like 158.63.258.200
Even though this IP is invalid, it can still cause issues.
Here’s what can happen:
- Network Troubleshooting Confusion: When invalid IPs appear in logs, IT teams waste time tracking something that doesn’t exist.
- Firewall Rule Errors: If someone mistakenly blocks or allows an invalid IP, firewall systems may throw errors or ignore rules.
- Security Alerts and False Positives: Security software may flag invalid IPs as suspicious, triggering unnecessary investigations.
- Broken Applications: Apps that rely on correct IP formatting may crash or fail if invalid IPs are input.
- Data Quality Issues: Invalid IPs reduce the reliability of analytics and monitoring systems.
Handling 158.63.258.200 in System Logs
If you find 158.63.258.200 in your logs, don’t panic.
Follow these steps:
Step 1: Confirm It’s Invalid
Use an IP validation tool or manually check octets:
258 ❌ invalid
Step 2: Identify the Source
Check:
- Server access logs
- Firewall logs
- Proxy reports
- Application error logs
Look for patterns like:
- Repeated entries
- Specific timestamps
- Linked user agents
Step 3: Check Misconfigurations
Review:
- NAT rules
- Routing tables
- Subnet masks
- VPN configuration
Step 4: Filter or Sanitize Data
Developers should sanitize IP inputs in code to prevent malformed entries.
Step 5: Monitor for Security Context
If the invalid IP appears alongside suspicious behavior, investigate deeper:
- Scanning attempts
- Bot activity
- Injection attacks
How to Validate and Fix IP Addresses?
Validation is essential in networking.
Tools to Validate IP Addresses
You can use:
- Online IP validators
- Network configuration tools
- Regex-based validation scripts
- Built-in OS commands
Manual Validation Rule
For IPv4, always ensure:
- Four octets
- Each between 0–255
- Proper dot separation
Example:
✅ 158.63.200.200
❌ 158.63.258.200
Fixing Invalid IPs
To fix an invalid IP:
- Re-check the intended address
- Replace octets above 255
- Update system configurations
- Correct application code
Security Implications of 158.63.258.200
Although invalid, this IP may still have security relevance.
Possible Security Interpretations:
- Bot-generated malformed traffic
- Misconfigured client requests
- Data corruption in logging systems
- Attempted obfuscation by attackers
Best Practice
Treat invalid IP entries as:
- A signal to validate systems
- A reason to improve log filtering
- A reminder to secure network inputs
Related Concepts Worth Knowing
To fully understand invalid IPs, it helps to know these concepts:
IPv4 vs IPv6
IPv4 is running out of addresses, which is why IPv6 was introduced.
Example IPv6:
2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334
IPv6 supports vastly more addresses and eliminates some IPv4 limitations.
Subnetting
Subnetting divides networks into smaller ranges.
Misconfigured subnetting may cause incorrect IP assignments.
TCP/IP Basics
IP works alongside TCP to deliver data packets across the internet reliably.
IP Lookup Tools
Valid IPs can be traced using WHOIS or geolocation tools.
Invalid IPs like 158.63.258.200 cannot.
The Shift from IPv4 to IPv6
Many competitor articles mention this shift, and it’s important for SEO completeness.
Why IPv6 Matters
- More address capacity
- Better routing efficiency
- Improved security features
- Future-proof networking
Still, IPv4 remains dominant today, meaning invalid IPv4 errors are still common.
Real-World Examples Involving Invalid IPs
Here are common scenarios:
Example 1: Web Server Logs
A server might record:
Client IP: 158.63.258.200
Error: Invalid format
This usually indicates parsing or user input errors.
Example 2: Firewall Configuration Mistake
Admin accidentally enters:
Block 158.63.258.200
Firewall rejects it due to invalid octet.
Example 3: Malware Scanner Reports
Some malware tools output malformed IPs when traffic data is corrupted.
FAQs:
1. Why is 158.63.258.200 not a valid IPv4 address?
158.63.258.200 is invalid because IPv4 addresses contain four octets, and each must fall between 0 and 255. The third octet “258” exceeds this limit, making the entire IP malformed.
2. Why does an invalid IP like 158.63.258.200 show up in server logs?
Invalid IPs can appear in server logs due to incorrect user input, misconfigured devices, corrupted log data, or software parsing issues. These entries often do not represent real network traffic.
3. Can 158.63.258.200 be linked to hacking or malicious activity?
While hackers usually spoof valid IP addresses, malformed IPs may still appear during automated scanning, bot traffic, or obfuscation attempts. However, most cases are caused by system errors, not attacks.
4. How can I validate whether an IP address is real or invalid?
To validate an IP address, check that it has four octets and each number stays within 0–255. Online IP validators, firewall tools, and network scripts can also quickly detect invalid formatting.
5. What should I do if I keep seeing 158.63.258.200 repeatedly?
If this invalid IP appears repeatedly, investigate the source by reviewing firewall logs, proxy reports, or application inputs. Ensure systems sanitize IP data and check for misconfigured network devices or scripts.
Conclusion:
158.63.258.200 may look like a normal IPv4 address, but it is invalid because one octet exceeds the permitted 0–255 range. Such malformed IPs often appear due to typing mistakes, log parsing errors, placeholder data, or misconfigured network devices. While usually harmless, they can cause confusion in troubleshooting and security monitoring. Understanding IPv4 rules, validating addresses properly, and filtering incorrect log entries helps maintain cleaner, safer, and more reliable network systems.







